 In SAP, Customer Master Data and Master Data Management are crucial. The accuracy of a transaction hinges on the precision of the Master Data. Transactions cannot proceed without properly maintained Master Data in the SAP system. If Master Data is inaccurately maintained, processes such as Procure-to-Pay, Order-to-Cash, Record-to-Report, Hire-to-Retire, and Plan-to-Produce will suffer. Inaccurate processing leads to unreliable reporting.
In SAP, Customer Master Data and Master Data Management are crucial. The accuracy of a transaction hinges on the precision of the Master Data. Transactions cannot proceed without properly maintained Master Data in the SAP system. If Master Data is inaccurately maintained, processes such as Procure-to-Pay, Order-to-Cash, Record-to-Report, Hire-to-Retire, and Plan-to-Produce will suffer. Inaccurate processing leads to unreliable reporting.
The significance of Master Data is evident in the fact that many companies allocate experienced and dedicated resources to their Master Data Management teams. These teams, often referred to as MDM teams, are composed of employees who focus exclusively on overseeing Master Data. They are tasked with entering precise data into designated fields and rigorously checking for any repetition, duplication, or redundancy in the Master Data.
Introduction to SAP Customer Master Data
Master data contains information that is always used in the same way. Master data forms the basis of sales and distribution processing. Data about the products as well as about the business partners (customers) are the basis for sales processing. Sales processing with the SAP ECC system requires that the master data is maintained in the system.
SAP Customer Master Data encompasses all the details about customers that need to be maintained in the system for future use. As implied by its name, it is the central repository for customer-related information. In SAP, whether you intend to sell finished goods, services, or even scrap, having a customer is essential for recording and executing sales transactions.
Customer Master Data can be classified as:
- Sales & Distribution Customer
- Finance or FI Customer
Let’s have a brief look on both types of Customers.
Sales & Distribution Customer
Sales & Distribution Customer is one whom you sell your manufactured or trading goods and services meaning the products which belong to your organization and for which you are known at the market. This type of Customer can also be used for the selling scrap materials, which is a regular feature in the organization, when you want to record and track the actual quantity of the scrap sold, if it has a significant accounting and financial impact.
Finance or FI Customer
Finance or FI Customer is one where you want to record sales to those customers who are not regular ones, not part of your regular sales and you do not offer your regular manufactured / trading goods and services to them. The example of such type of customers can be, but not limited to, customers to whom you sell your fixed assets after they were completely depreciated. Like you have a machinery which has reached the end of its technical life and now you want to scrap it. Similarly, some companies offer vehicles for sale which the company has been using for quite some time to their employees first before offering it for sale at the open market.
In short, those customers who are not part of regular sales and for whom there is no requirement to maintain Sales & Distribution’s specific data.
Account Groups in SAP Customer Master Data
Account Groups in Customer Master Data are used for high level classification of Customers. It helps you to classify your customers based on different traits, sector or line of business. It also helps to decide which fields are mandatory when you are creating a customer related to a certain sector, which fields are optional and which fields can be suppressed or made hidden so that the User at the time of Customer creation doesn’t get confused.
Example: You can make Value Added Tax – VAT field mandatory in the Account Group of a regular customer, so that the system doesn’t let the User to bypass the said field until and unless it is populated.
Under Account Groups you can configure in the backend and define if a certain Account Group’s Customer number can be assigned internally / automatically by the SAP system or externally by the User at the time of Customer creation or specific number range for a specific customer or whether the Customer’s Account Group number range is either numeric or alphanumeric.
Classification of SAP Customer Master Data
Customer master is a centrally shared data which can be used by the logistics modules as well as the finance module. Information contained in the customer master record can be both descriptive and have functional control depending on the usage. Customer Master Data is classified in following three views:
General Data
General Data in the Customer Master that is relevant for both Sales & Distribution and Accounting, the data fields are grouped on several tab pages. The general data includes Name, Address, Telephone number, other contact details, VAT, Tax, Good Receiving Hours of Customer, Market Standing of the Customer, Correspondence, Contact Persons with their designation and contract detail, etc.
Company Code Data
Company Code Data is relevant for Financial Accounting purposes and processes. It is specific for a given Company Code. This view records data of the Customer’s Accounting Data such as reconciliation account, sort rule, payment terms, withholding tax information, payment methods, correspondence information with the customer, dunning, insurance, etc.
Company Code data only applies to one Company Code. This data is only relevant to Financial Accounting and includes:
- Account Management
- Payment Transactions
- Correspondence
- Insurance
If you edit a master record, you must specify the customer number and a company code to access the screens containing company code data. You can only invoice a business transaction if the data on the Payer partner function is entered in the Financial Accounting view.
Sales Area Data
Sales Area Data is relevant for Sales and Distribution processes and is specific to a given Sales Area. You can maintain the Sales Area Data in various ways, depending on the Sales Area (a combination of Sales organization, Distribution channel and Division). All the sales related information will be maintained in this area. Including Sales, Shipping, Billing and Partner Function. All the data present in the system will be applicable only for that specific sales area. The customer can be extended for any other sales area as well depending upon business requirements.
This view is to record the data of customer related to Sales and Distribution transaction such as data for sales process, delivery process, billing process and partner function. The data for one customer can differ for each sales area. This data is only relevant to Sales and Distribution. If you edit a Customer Master record, you must enter the Customer number and the Sales Area to access screens containing Sales and Distribution data. You can only process Sales and Distribution transactions, for example, a sales order, after entering the Sales and Distribution data for a Customer in the Customer Master Data.
All critical fields that must be maintained by the business in the system are set as mandatory fields, so that the users will not forget to enter all the necessary data during the sales transaction(s). Sales Area data of customers is further classified in following four tabs/sections:
- Sales
- Shipping
- Billing
- Partner Functions
Important SAP Customer Master Data Transactions
Following is the list of the key transaction related to SAP Customer Master Data:
- VD01 – Create Sales & Distribution Customer Master
- VD02 – Change Sales & Distribution Customer Master
- VD03 – Display Sales & Distribution Customer Master
- VD04 – Display Changes Sales & Distribution Customer Master
- VD05 – Block Sales & Distribution Customer Master
- VD06 – Flag for Deletion Sales & Distribution Customer Master
- FD01 – Create Accounting Customer Master
- FD02 – Change Accounting Customer Master
- FD03 – Display Accounting Customer Master
- FD04 – Display Changes Accounting Customer Master
- FD05 – Block / Unblock Accounting Customer Master
- FD06 – Set Deletion Indicator Accounting Customer Master
- XD01 – Create Customer Master – Centrally / Complete
- XD02 – Change Customer Master – Centrally / Complete
- XD03 – Display Customer Master – Centrally / Complete
- XD04 – Display Changes Customer Master – Centrally / Complete
- VCUST – Customer List
How to Create SAP Customer Master Data
As always, there are several ways to start a transaction in SAP ERP:
- Enter XD01 in Transaction Command Field or executing Customer Master Creation Transaction
- Navigate through ‘Tree’
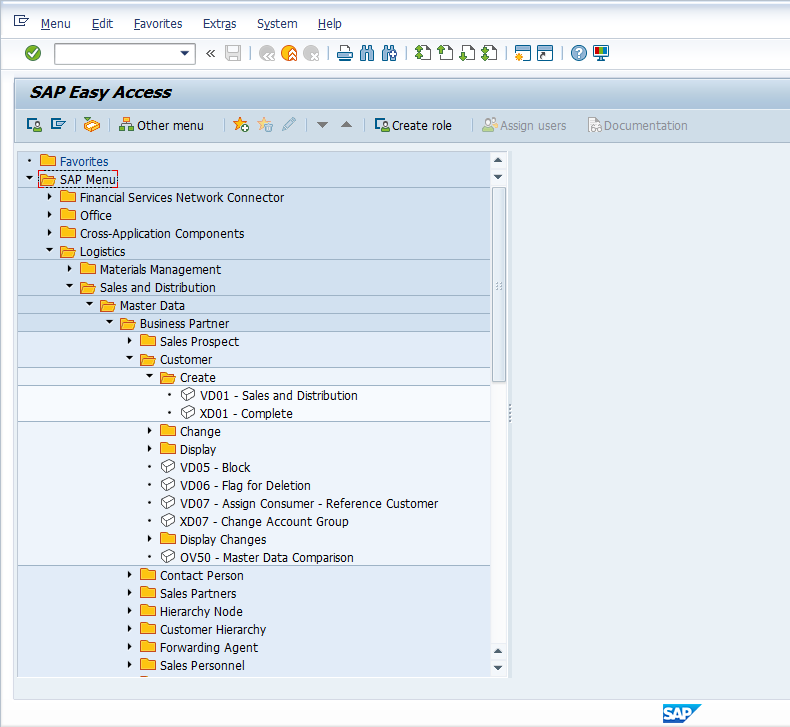
Create SAP Customer Master Data Centrally
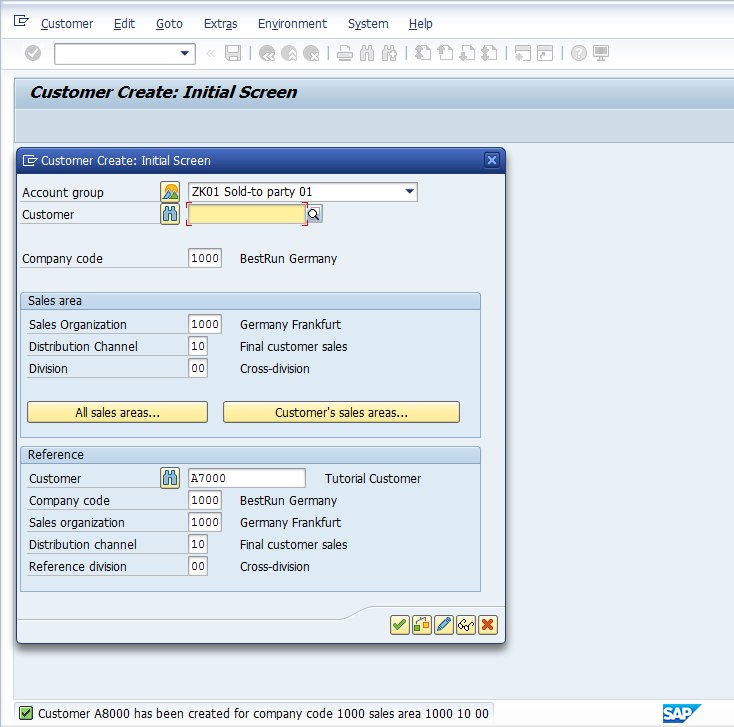
Whenever you want to create Customer Master Data, enter XD01 to create Customer Master complete / centrally.
In the initial screen, a dialog box will appear:
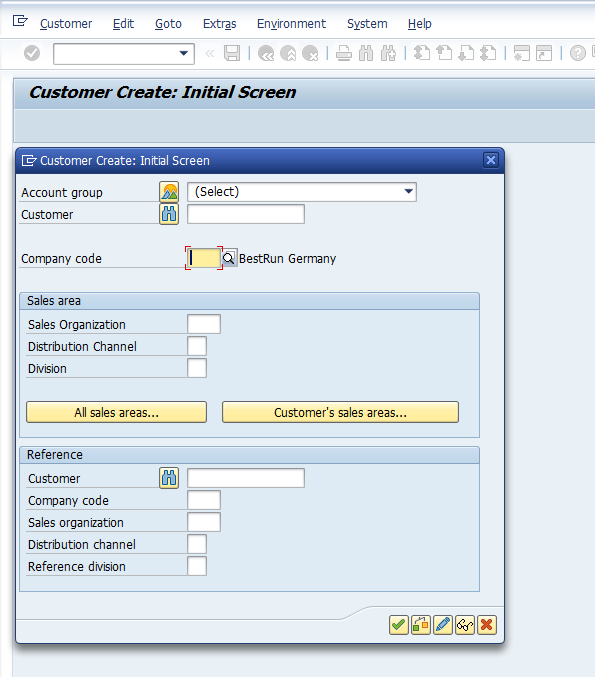
In the first part of the dialog box, you should select the relevant Account Group. List of all Account Groups will be displayed:
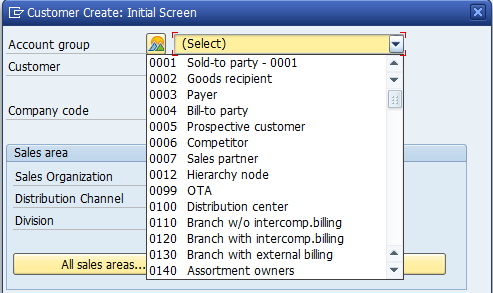
Select the relevant Account Group and populate relevant Company Code, Sales Organization, Distribution Channel and Division. Since this Account Group has a setting of ‘external’ number range which is alphanumeric, therefore, enter the Customer code as well. Else in other case where number range is internal this field needs to be blank.
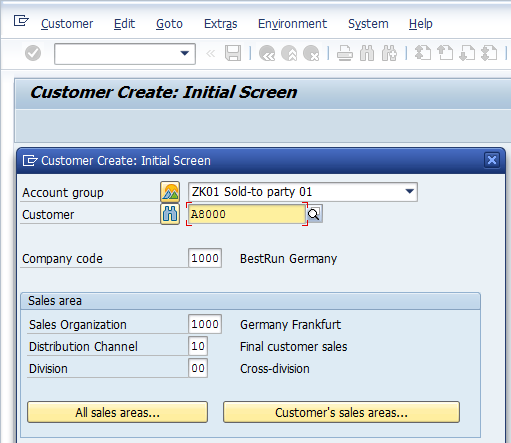
If you do not populate the Customer field the system will prompt with following message:
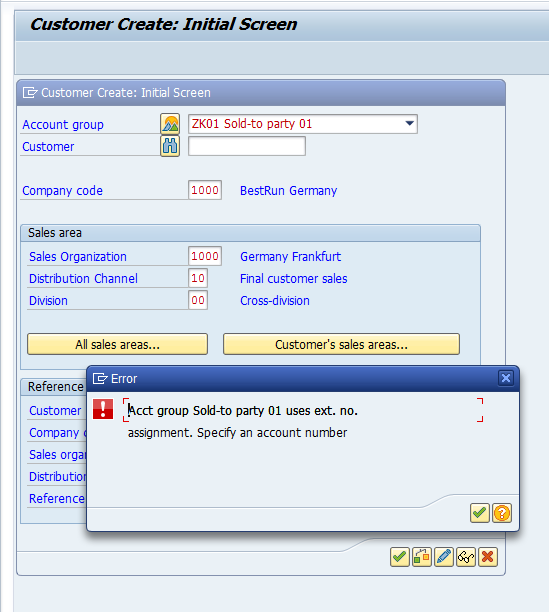
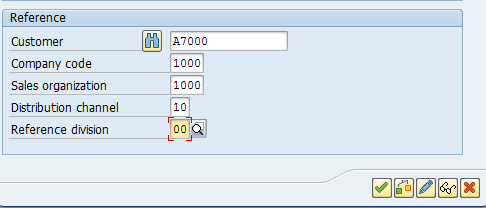
If you want to reference the Customer which is already created in the system and is very close to the nature of the Master Data you are about to create, you can use the second section ‘Reference’ of the dialog box on the initial screen. This step will help and assist you in populating required fields as they will be copied from the reference Customer, except the basic information i.e. name, phone, etc. which will help in easing the data entry. You can change the default populated fields, where required.
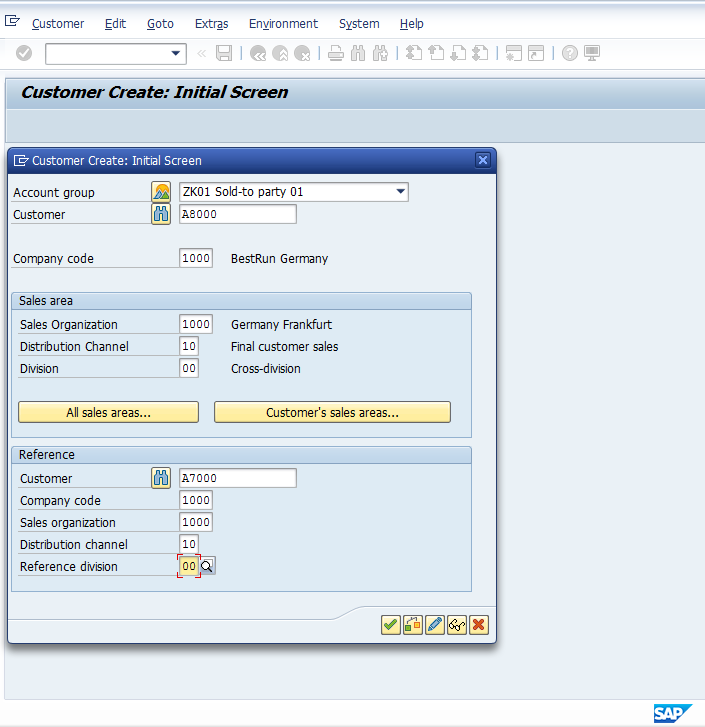
Once you have populated all the required fields, press either enter or ![]() at the end of the dialog box.
at the end of the dialog box.
SAP Customer Master – General Data
The system will take you the first tab of the General Data where you are required to enter Customer’s basic information, i.e. Address, Telephone Number, Email, etc.
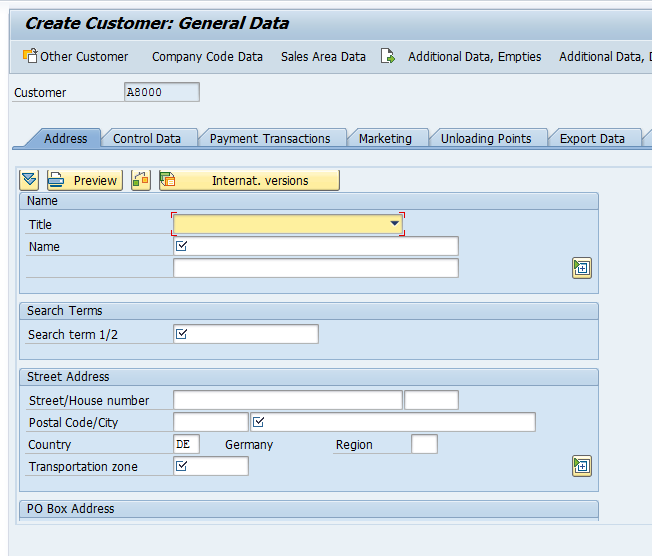
Please note the fields ![]() having a check box are required fields. If they are not populated, the system will prompt with an error message
having a check box are required fields. If they are not populated, the system will prompt with an error message ![]() .
.
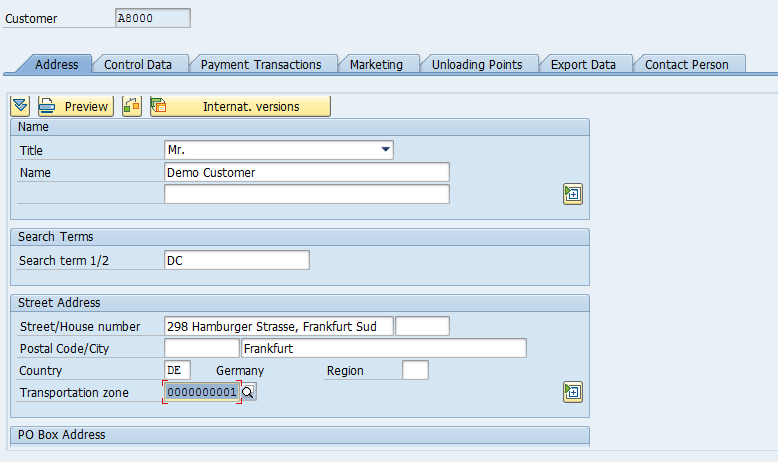
Enter Name, Address and Search Term. Search Term helps in finding relevant Customer at the time of Sale Order Entry in the Search Help dialog box. Enter required fields, when you press ‘More Fields’ ![]() button, system will show additional fields:
button, system will show additional fields:
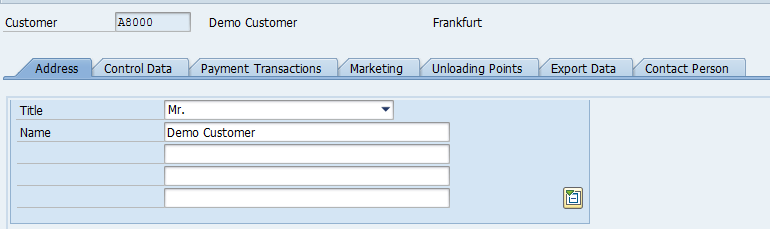
Scroll to other Tabs in General Data and populate data where required.
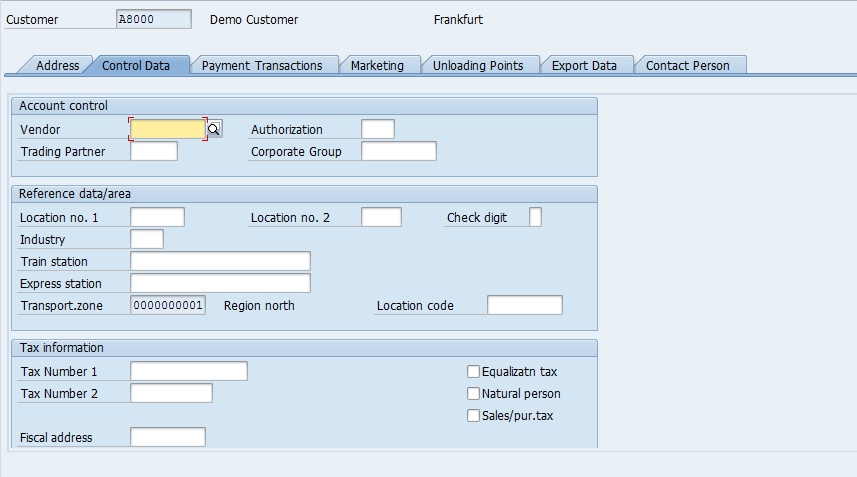
If your customer is also your Vendor, you can enter the Vendor number of Vendor Master in the Vendor field.
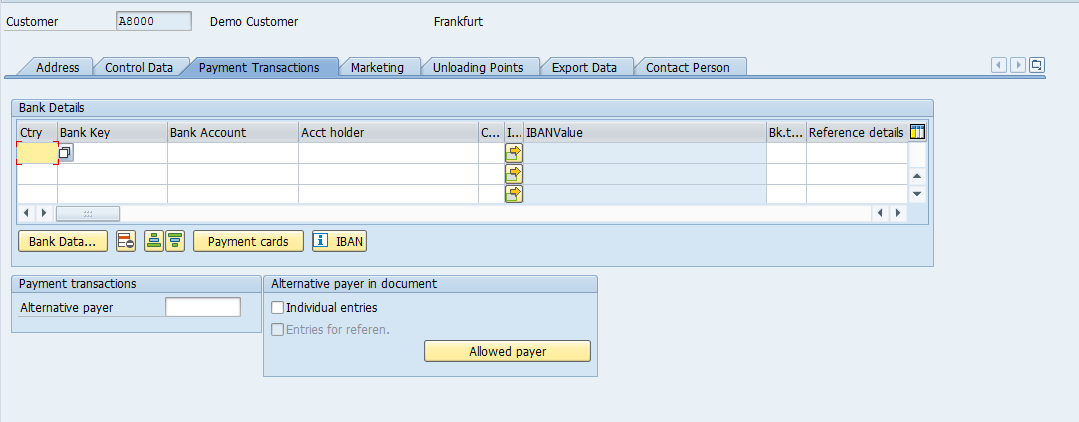
Bank Information of the Customer:
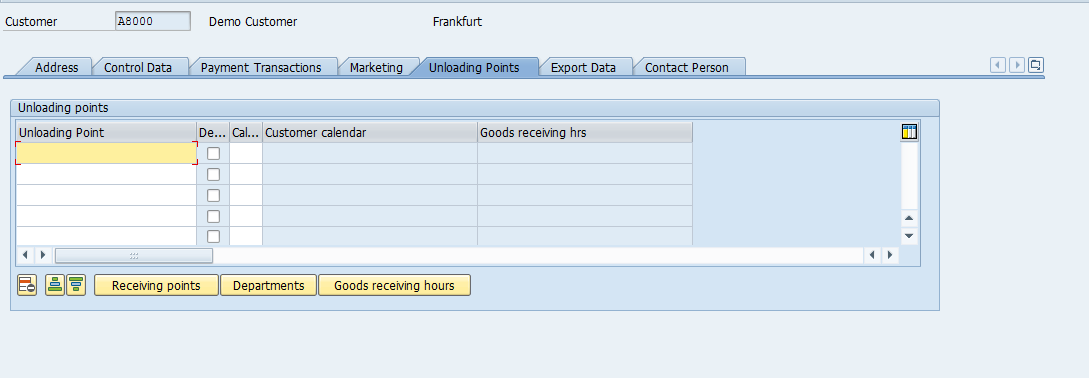
Good receiving hours of the Customer are maintained here:
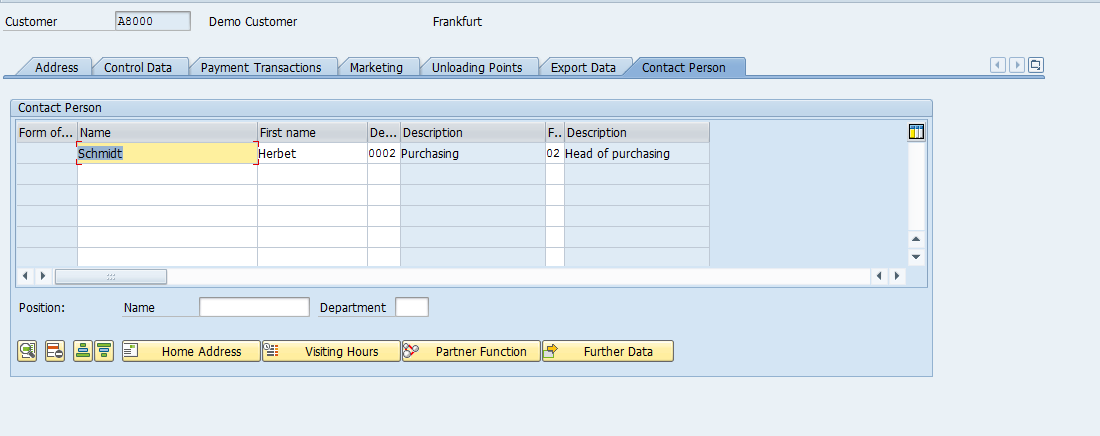
SAP Customer Master – Company Code Data
Press ![]() button to enter the Company Code Data view.
button to enter the Company Code Data view.
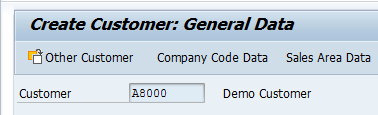
Since this Customer is created with reference, hence, fields of Reconciliation Account and Sort Key are already populated.
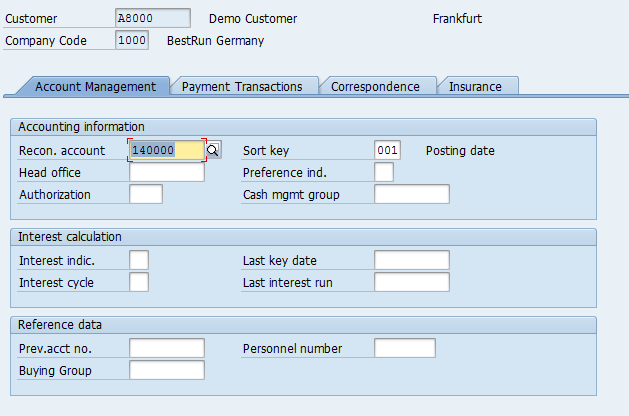
SAP Customer Master – Sales Area Data
Press ![]() button to enter the Sales & Distribution data view.
button to enter the Sales & Distribution data view.
The first tab you will arrive is ‘Sales’. It contains sales related information.
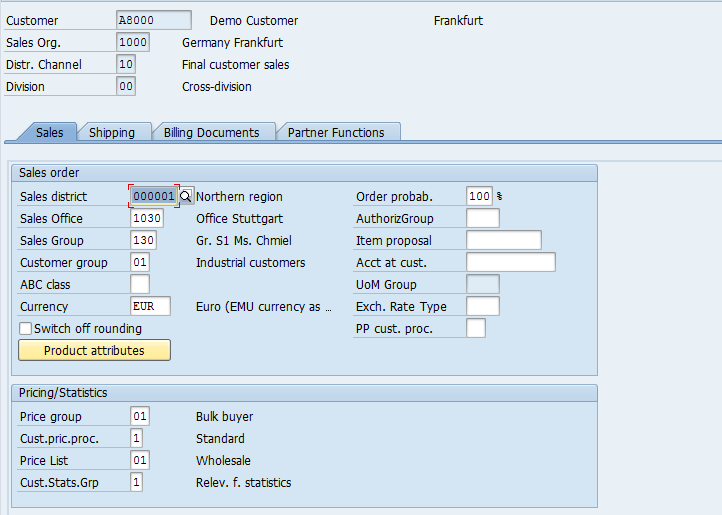
Sales District – A geographical segmentation which defines a higher level of sales geographical structure.
Sales Office – Sales Office establishes connection between the company and the customer. It monitors company’s sales in the market which is done by company’s sales force. It is a physical location that has the responsibility of the sale of certain products or services within a given geographical area.
Sales Group – A sales office can be sub divided into sales groups.
Customer Group – Identifies a group of customers (for example, wholesale or retail).
Currency – the currency in which the customer order goods.
Acct at cust. – Your Vendor or account number which the Customer uses in their organization for various purposes.
Price group – which pricing group does the customer belongs, for pricing condition purposes.
Cust.pric.proc. – for determination of correct pricing structure on Sales Order.
Price List – the pricing classification to which the customer belongs.
Cust.Stats.Grp – for generating SIS (LIS) reporting.
The second tab is of ‘Shipping’ which is relevant at the time of delivery / dispatch or shipment of goods to the Customer.
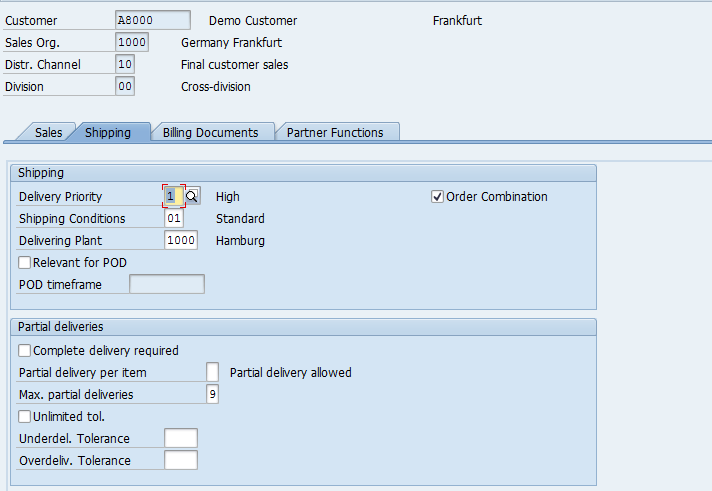
Delivery Priority – High, Normal, Low, Medium.
Shipping Conditions – Standard or Immediately.
Delivering Plant – Plant from which the goods to be dispatched to the Customer.
Complete Delivery – if the Customer only accepts complete deliveries and partial is not allowed. This check box needs to be checked if Customer doesn’t accept partial deliveries.
Partial delivery per item – whether partial deliveries are allowed.
Max. partial deliveries – the number of maximum partial deliveries are allowed.
Unlimited tol. – if the customer accepts unlimited over or under deliveries of goods ordered.
Underdel. Tolerance – Percentage (based on the order quantity) up to which an under delivery is accepted by the Customer.
Overdeliv. Tolerance – Percentage (based on the order quantity) up to which an over delivery is accepted by the Customer.
The third tab of the Sales Area Data is ‘Billing’:
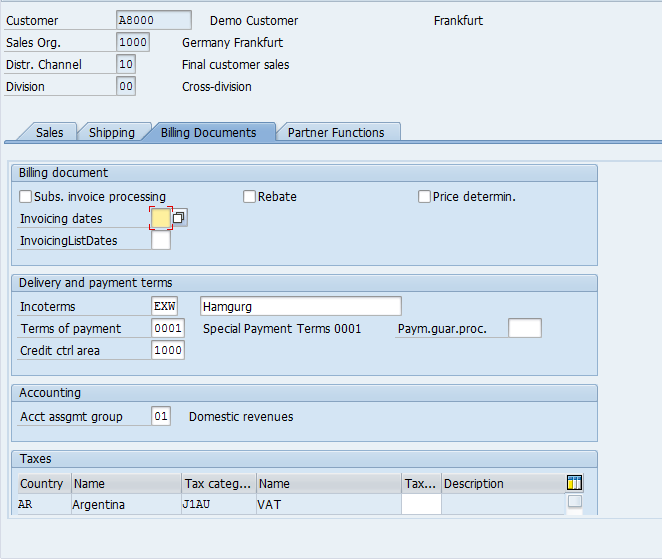
It contains information whether the Customer is relevant for Rebates.
Incoterms – trading established globally with the standard of International Chamber of Commerce (ICC)
Terms of payment – agreed terms of payment with the Customer weather is Customer is a Cash or Credit.
Paym.guar.proc. – Payment Guarantee Procedure defines if the Customer pays via Letter of Credit, Payment Cards or Bank Guarantee.
Credit ctrl area – Credit Control Area, if the Customer is a Credit Customer and belongs to a Credit Control Area.
Taxes – if the customer is liable for Taxes or exempted etc.
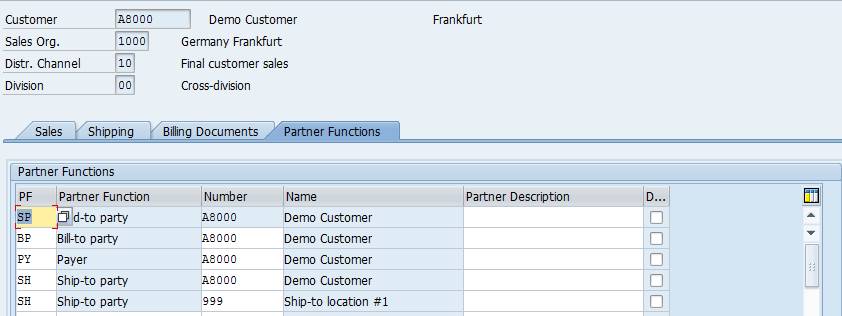
The fourth and the final tab is Partner Functions:
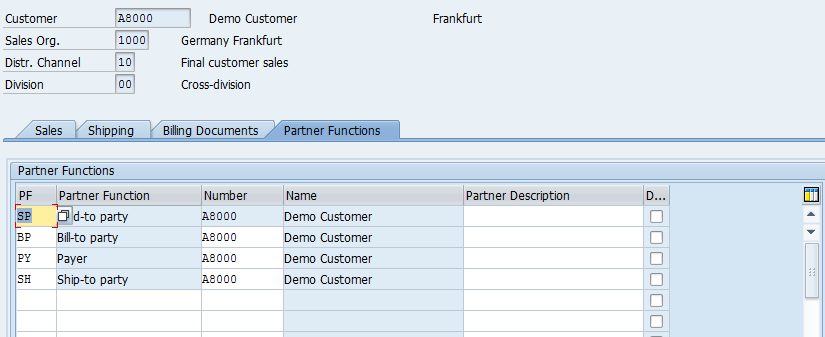
It shows the parties involved in the sales processing. The following are the mandatory partner functions:
- Sold to Party
- Bill to Party
- Payer
- Ship to Party
If the Customer has multiple locations where he ordered the goods to be delivered, you can add Ship to Parties here in this tab. Please note that the Ship to Party Master Data should be created under relevant Account Group.
Once you are done with maintaining and changing values in the SAP Customer Master Data, don’t forget to press Save ![]() or CTRL+S for the values to take effect in your sales transactions and the system will confirm that the Customer is created and saved.
or CTRL+S for the values to take effect in your sales transactions and the system will confirm that the Customer is created and saved.
—
Did you find this tutorial helpful? If you have any questions or comments, we would appreciate your feedback in the comments section below. Your input would be greatly beneficial to us, and it may be something we can incorporate to enhance our free SAP SD tutorials.